Alexander 2014 宇宙早期黑洞质量快速增长的模型
主要内容:
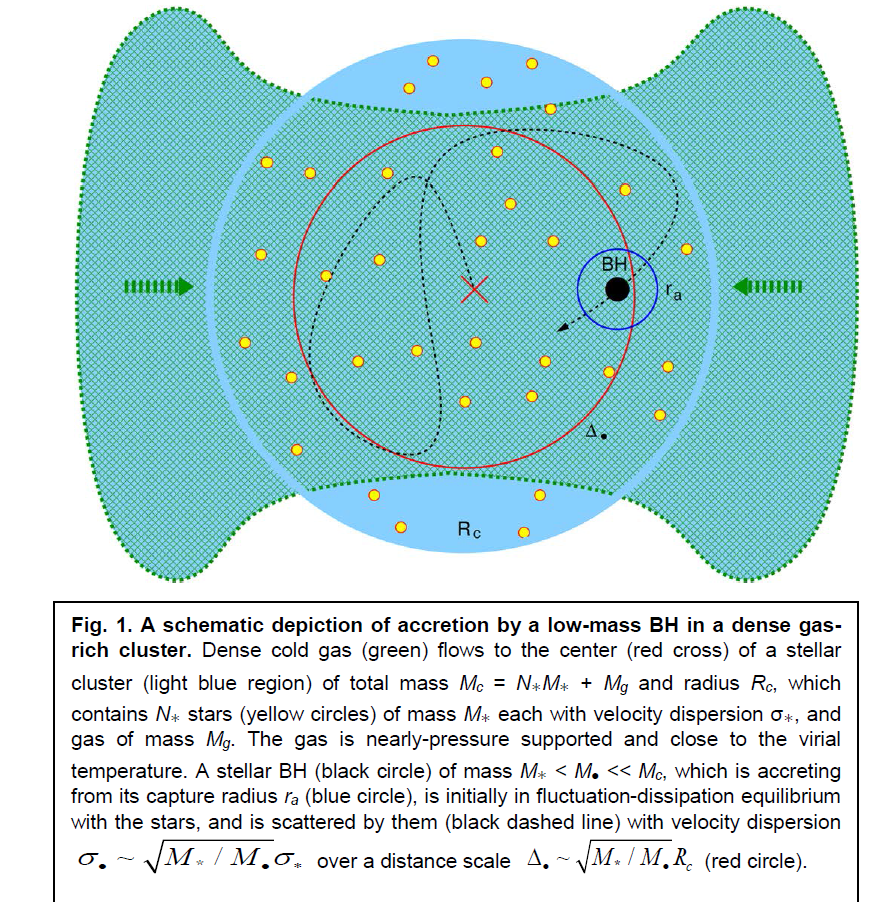
在密的star claster 里的比较小质量的黑洞,不会马上 形成吸积盘(吸积盘的吸入速度太慢),而是由于黑洞的质量小不占主导,在cluster中在做 无规运动,不 形成盘,物质直接 掉入,快速增长质量。而由于当地密度太大,光深大,引力能释放产生的光子出不来,所以也看不到。
话说这篇文章出来,是不是意味着AGN中黑洞质量来源之谜就解决了?
精彩摘抄:
文章信息:
http://www.sciencemag.org/content/early/2014/08/06/science.1251053.abstract
Rapid growth of seed black holes in the early universe by supra-exponential accretion
+ Author Affiliations
- ↵*Corresponding author. E-mail: tal.alexander@weizmann.ac.il
Mass accretion by black holes (BHs) is typically capped at the Eddington rate, when radiation's push balances gravity's pull. However, even exponential growth at the Eddington-limited e-folding time tE ~ few×0.01 Gyr, is too slow to grow stellar-mass BH seeds into the supermassive luminous quasars that are observed when the universe is 1 Gyr old. We propose a dynamical mechanism that can trigger supra-exponential accretion in the early universe, when a BH seed is trapped in a star cluster fed by the ubiquitous dense cold gas flows. The high gas opacity traps the accretion radiation, while the low-mass BH's random motions suppress the formation of a slowly draining accretion disk. Supra-exponential growth can thus explain the puzzling emergence of supermassive BHs that power luminous quasars so soon after the Big Bang.
- Received for publication 20 January 2014.
- Accepted for publication 21 July 2014.

没有评论:
发表评论