Dall'Osso 2010 中子星spin down的能量注入解释X射线余辉变平
主要内容:
精彩摘抄:
文章信息:
· Find Similar Abstracts (with default settings below) - · arXiv e-print (arXiv:1004.2788)
- · References in the Article
- · Citations to the Article (1) (Citation History)
- · Refereed Citations to the Article
- · Also-Read Articles (Reads History)
- ·
- · Translate This Page
| Title: | GRB Afterglows with Energy Injection from a spinning down NS | |
| Authors: | Dall'Osso, Simone; Stratta, Giulia; Guetta, Dafne; Covino, Stefano; De Cesare, Giovanni; Stella, Luigi | |
| Publication: | eprint arXiv:1004.2788 | |
| Publication Date: | 04/2010 | |
| Origin: | ARXIV | |
| Keywords: | Astrophysics - High Energy Astrophysical Phenomena | |
| Comment: | 7 pages, 2 figures, submitted to Astronomy & Astrophysics - referee's comments included | |
| Bibliographic Code: | 2010arXiv1004.2788D |
Abstract
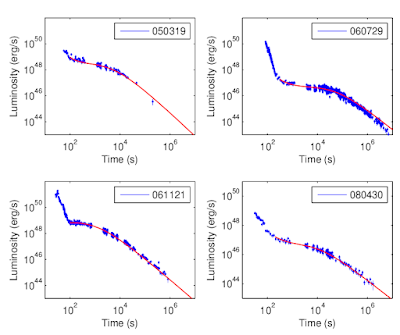
We investigate a model for the shallow decay phases of Gamma-ray Burst (GRB) afterglows discovered by Swift/XRT in the first hours following a GRB event. In the context of the fireball scenario, we consider the possibility that long-lived energy injection from a millisecond spinning, ultramagnetic neutron star (magnetar) powers afterglow emission during this phase. We consider the energy evolution in a relativistic shock subject to both radiative losses and energy injection from a spinning down magnetar in spherical symmetry. We model the energy injection term through magnetic dipole losses and discuss an approximate treatment for the dynamical evolution of the blastwave. We obtain an analytic solution for the energy evolution in the shock and associated lightcurves. To fully illustrate the potential of our solution we calculate lightcurves for a few selected X-ray afterglows observed by Swift and fit them using our theoretical lightcurves. Our solution naturally describes in a single picture the properties of the shallow decay phase and the transition to the so-called normal decay phase. In particular, we obtain remarkably good fits to X-ray afterglows for plausible parameters of the magnetar. Even though approximate, our treatment provides a step forward with respect to previously adopted approximations and provides additional support to the idea that a millisecond spinning (1-3 ms), ultramagnetic (B$\sim 10^{14}-10^{15}$ G) neutron star loosing spin energy through magnetic dipole radiation can explain the luminosity, durations and shapes of X-ray GRB afterglows.| Bibtex entry for this abstract Preferred format for this abstract (see Preferences) |

没有评论:
发表评论